Why Wax Appearance Temperature Matters for Oil and Gas Producers
“Hot or cold? When it comes to the production and transportation of oil and gas, this question is more than just a matter of personal preference. The wax appearance temperature (WAT) plays a crucial role in determining whether your operations will run smoothly or come to a standstill. In this blog post, we’ll dive into why WAT matters for oil and gas producers and how understanding it can save you time, money, and headaches.”
What is Wax Appearance Temperature?
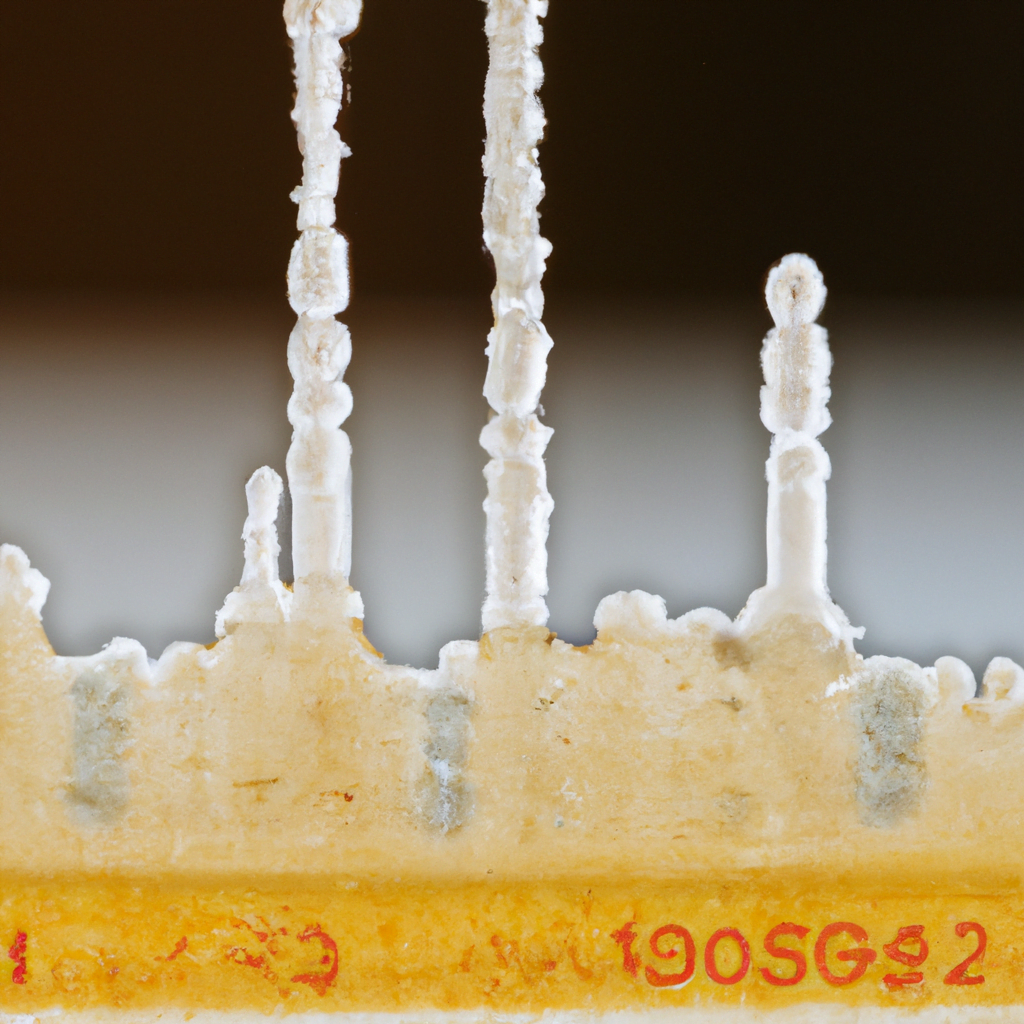
As anyone in the oil and gas industry knows, Wax Appearance Temperature (WAT) is the temperature at which wax crystals first appear in a crude oil sample when cooled under controlled conditions. The significance of this property was first realized in the early 1900s when it was observed that the pour point of a crude oil was usually about 10°C lower than its WAT. Pour point is defined as the temperature above which an oil will flow when cooled under specified conditions.
Why does Wax Appearance Temperature Matter for Oil and Gas Producers?
Wax appearance temperature (WAT) is an important quality parameter for crude oil and petroleum products. It is the temperature at which the first crystals of wax appear when cooling a hot oil sample. The WAT is closely related to the pour point, which is the temperature at which the oil becomes thick and sluggish. Both the WAT and pour point are affected by the presence of wax in the crude oil.
Waxes are natural compounds that are found in crude oils. They are composed of long-chain hydrocarbons with high melting points. At low temperatures, these waxes solidify and can clog pipes and other equipment. This can cause serious problems for oil and gas producers who must operate in cold climates.
The WAT gives producers an indication of how much wax is present in a crude oil sample and how it will behave at low temperatures. For example, a crude oil with a high WAT will have less wax precipitate out at lower temperatures than a crude oil with a low WAT. This information is important for deciding where to site production facilities, what type of equipment to use, and how to transport the product.
In general, light crudes have lower Wax Appearance Temperatures than heavy crudes. But there are many other factors that can affect the WAT of a particular crude oil sample, such as its geologic origin, degree of processing, and impurities present
How to Test for Wax Appearance Temperature
The oil and gas industry is all about production. But, in order for production to happen, there needs to be a product that meets certain specifications. Quality control is important in any industry, but it’s especially critical in the oil and gas industry where a mistake can be costly.
One of the quality control tests that oil and gas producers use is the wax appearance temperature test. This test measures the temperature at which wax crystals first appear in crude oil. The results of this test can tell producers a lot about the quality of their product.
There are two main methods for testing wax appearance temperature: the cold filter plugging point test and the pour point test. Both of these tests involve cooling a sample of oil until wax crystals begin to form. The cold filter plugging point test measures the temperature at which 50% of the oil sample is blocked by wax crystals. The pour point test measures the lowest temperature at which the oil will flow.
Wax appearance temperature is important because it can indicate whether an oil sample has too much or too little paraffin content. Paraffin is a type of wax that is found in crude oil. It’s made up of long-chain hydrocarbons, and it’s what gives crude oil its waxy texture and appearance.
If an oil sample has a low wax appearance temperature, it means that there is not enough paraffin present. This can cause problems during production because the lack of paraffin can lead
The Impact of Wax Appearance Temperature on Oil and Gas Production
It is well known that the appearance temperature of wax can have a significant impact on oil and gas production. For example, if the appearance temperature of wax is too low, it can cause pipeline blockages and other problems. On the other hand, if the appearance temperature of wax is too high, it can lead to decreased production and increased operational costs.
In order to optimize production, it is important for oil and gas producers to understand the impact of wax appearance temperature on their operations. By understanding how different appearance temperatures can affect production, they can make adjustments to their processes to ensure that they are operating at optimal levels.
Conclusion
Wax appearance temperature is an important parameter to consider when producing oil and gas. By monitoring this temperature, producers can optimize production rate, avoid crystallization in pipelines and improve the performance of their products. As the wax appearance temperature increases, so does its viscosity which makes it easier to pump through long-distance pipelines with ease. With this knowledge in hand, producers can now make more informed decisions about how best to produce their oils and gases for maximum efficiency and profitability.